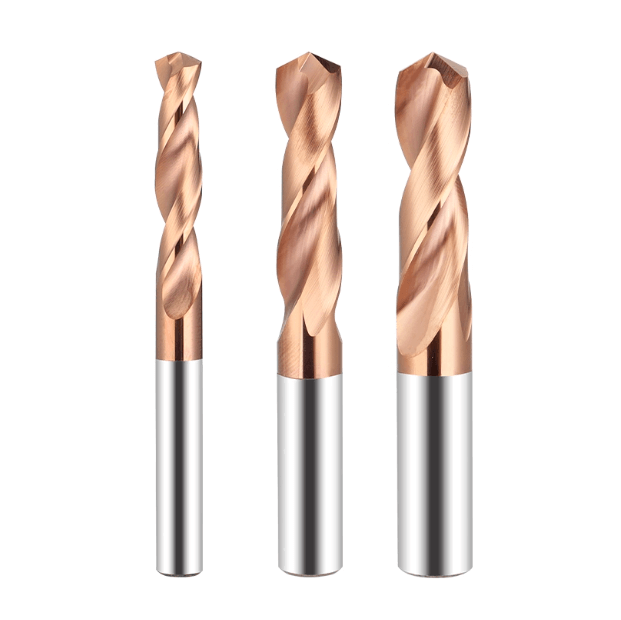
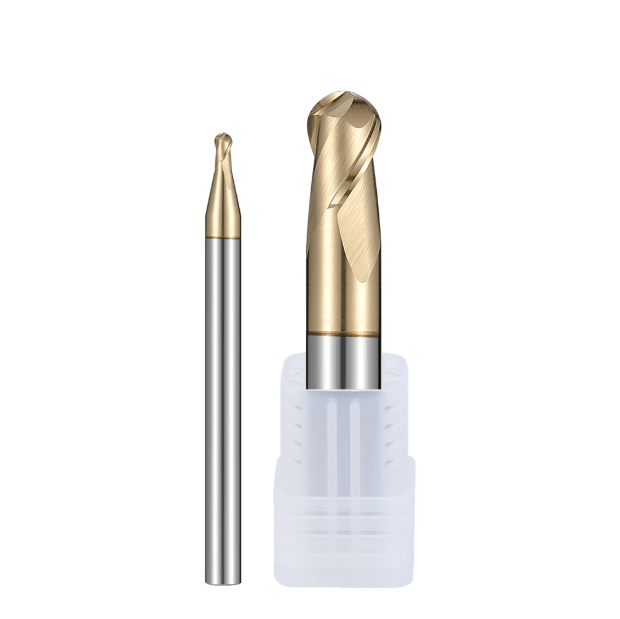
In today’s metalworking industry, where precision and efficiency continue to advance, selecting the best drill bits for drilling metal has become a key factor influencing machining stability and final part quality. Faced with different metal materials, drilling depths, and production requirements, users must not only choose from a wide range of drill bit types but also make accurate decisions among more specialized solutions such as carbide drill bits for metal, long drill bits for metal, and deep hole drilling tools for metal. As the market places greater emphasis on chip evacuation, wear resistance, feed rate optimization, and tool-life stability, the structural design, substrate material, and coating performance of drill bits have become critical indicators of machining efficiency.
In practical applications, carbide drill bits stand out for their exceptional hardness and heat resistance, making them suitable for high-strength metals and continuous, long-cycle machining. Long drill bits address deep-hole applications by offering improved rigidity, better chip evacuation, and more consistent bore accuracy. Deep hole drilling tools, widely used in mold manufacturing, hydraulic components, aerospace parts, and structural steel machining, provide irreplaceable advantages in terms of machining stability and drilling depth. For companies requiring mass production or customized cutting tools, partnering with a reliable OEM drill bit supplier for metal machining is essential for achieving precise tool compatibility, cost control, and stable production efficiency.

Core Selection Criteria for Metal Drilling Tools in 2025
When selecting the best drill bits for drilling metal, the metalworking environment of 2025 demands higher levels of stability, wear resistance, and compatibility with a variety of materials. With the increasing use of high-strength steels, stainless steels, and titanium alloys, drill bits must support higher cutting speeds, longer tool life, and more reliable chip evacuation. To maintain consistent bore quality under different machining conditions, users typically evaluate drill bits by substrate material, geometry, coating, chip-flute design, and compatibility with machine tool rigidity and cooling systems. Furthermore, many companies choose trusted OEM drill bit suppliers for metal machining to ensure that tool configurations align precisely with production needs.
The Impact of Metal Drill Bit Material Properties on Machining Quality
The material composition of a metal drill bit directly affects hardness, heat resistance, and resistance to chipping or edge failure. Common materials include high-speed steel, cobalt steel, and cemented carbide. Among these, carbide shows the highest stability in difficult-to-machine metals, making carbide drill bits for metal the preferred choice for high-performance drilling. Carbide maintains edge sharpness during high-speed drilling, resulting in smoother surfaces, reduced burr formation, and lower thermal deformation. In batch production or long-cycle drilling tasks, the stability of the drill bit material directly determines hole consistency and long-term quality control.
Matching Drill Bit Cutting Edge, Rake Angle, and Metal Type
Drill bit geometry—including cutting edge shape, clearance angle, point angle, and flute design—plays a decisive role in drilling performance. Different metals require different rake angles and point angles. Soft metals need larger rake angles for smoother cutting, while high-hardness materials require larger point angles for better edge strength. Correct geometry selection improves drilling accuracy, lowers cutting resistance, and reduces premature tool wear. In deep-hole applications—such as when using long drill bits for metal or specialized deep hole drilling tools—flute design and edge structure are especially important, as insufficient chip evacuation can lead to overheating, hole wall scratches, or drilling interruption.
The Role of Coating Technology in Extending Tool Life
Modern metal drill bits rely heavily on advanced coating technology. Coatings such as TiN, TiAlN, AlTiN, and DLC significantly improve wear resistance, heat resistance, and anti-adhesion performance. High-quality coatings maintain edge sharpness under high-speed or high-hardness conditions, reduce friction, and ensure consistent performance even during deep-hole drilling or continuous mass production. For materials like stainless steel and heat-resistant alloys, selecting drill bits with advanced coatings is essential for maintaining hole quality and reducing machining costs. When choosing the best drill bits for drilling metal, the coating quality often becomes a high-priority factor.

Main Types and Application Scenarios of the Best Drill Bits for Drilling Metal
Selecting the correct drill bit type is critical for ensuring machining efficiency, stability, and consistent quality. Different materials, drilling depths, equipment types, and cooling environments require different tool structures. When evaluating the best drill bits for drilling metal, users consider drill bit material, coating, flute design, chip evacuation capability, machining depth, and compatibility with manual or CNC equipment. Manufacturing companies often rely on OEM drill bit suppliers for metal machining to ensure that tool specifications precisely match production requirements.
High-Performance Drill Bit Configurations for General Metal Machining
For common metals such as carbon steel, aluminum, copper, and general alloys, high-performance drill bits made from reinforced high-speed steel or cobalt steel are widely used. Equipped with optimized cutting edge geometry and effective heat-resistant coatings, these drill bits deliver stable performance under medium to high spindle speeds. Their versatility and durability make them suitable for most general metalworking applications, striking a balance between cost and performance.
Professional Solutions for Hardened Steel, Stainless Steel, and Difficult Materials
Difficult-to-machine materials such as hardened steel, stainless steel, titanium alloys, and heat-resistant alloys require drill bits with higher hardness and thermal stability. Carbide drill bits for metal are the mainstream solution in these applications due to their ability to maintain edge strength under high pressure and high temperature. Reinforced cutting tips, optimized chip flutes, and high-temperature coatings reduce cutting resistance, prevent cold welding, and significantly extend tool life under continuous high-load drilling.
Performance Requirements for Batch Production vs. Precision Machining
Batch production emphasizes cost control and tool life consistency, favoring drill bits with strong wear resistance, stable chip evacuation, and extended service intervals. Tools with internal cooling and advanced coatings are commonly used. Deep-hole and long-hole machining scenarios—such as when using long drill bits for metal or deep hole drilling tools—require exceptional cooling and chip removal capability.
Precision machining, in contrast, places greater emphasis on dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and flawless cutting stability. These applications often require tighter cutting edge tolerances, higher coating consistency, and premium carbide substrates. Many companies rely on custom or OEM drill bit solutions to meet these strict requirements.

Advantages and Key Usage Points of Carbide Drill Bits for Metal
Carbide drill bits have become essential tools for high-strength metal drilling due to their exceptional hardness, heat resistance, and overall stability. As industries continue to demand higher drilling speeds, better surface quality, and longer tool life, carbide drill bits for metal are increasingly replacing traditional high-speed steel and cobalt drill bits. Whether used for difficult materials, high-speed CNC drilling, deep holes, or automated production, carbide provides stable, efficient, and repeatable results.
Stability Advantages When Machining High-Hardness Metals
Carbide drill bits, sintered from tungsten carbide and metallic binders, offer high compressive strength and excellent edge retention. This makes them ideal for hardened steels, stainless steels, and nickel-based alloys. Carbide reduces hole wall roughness, minimizes chipping risk, and maintains accuracy even under high-temperature, high-pressure conditions. This stability is crucial for demanding applications such as “carbide drills for hardened steel” or “carbide drills for stainless steel.”
Heat Resistance and Chipping Resistance in High-Speed CNC Machining
High-speed drilling is now fundamental in modern machining, and carbide drill bits are the primary tools enabling it. Supported by advanced coatings such as AlTiN and TiAlN, carbide maintains edge strength within high-temperature zones, minimizing thermal wear. In aerospace components, stainless steel structures, and mold steel machining, carbide drill bits deliver excellent chipping resistance, dimensional stability, and hole quality—making them indispensable in high-speed metal drilling setups.
Maximizing the Lifespan of Carbide Drill Bits for Metal in Mass Production
To achieve the longest tool life in mass production environments, several factors must be optimized:
Selecting Proper Cutting Parameters
Choose spindle speed and feed rate based on metal hardness, depth of cut, and equipment rigidity to prevent overheating and chipping.
Using Appropriate Cooling Methods
Internal coolant supply is critical for deep-hole drilling and continuous high-speed operations.
This is especially important for deep hole drilling tools for metal.
Optimizing Chip Evacuation
For long-hole or deep-hole machining, inadequate chip flow leads to heat buildup. Long drill bits for metal require effective flute design and proper lubricant supply.
Ensuring Workpiece and Machine Stability
Workpiece clamping, machine rigidity, and spindle runout directly affect tool life in production scenarios.
Choosing a Reliable OEM Supplier
Working with a consistent OEM drill bit supplier for metal machining ensures uniform tool quality and eliminates performance fluctuations between batches.
Through proper parameter control, tool selection, and machining management, carbide drill bits for metal deliver significantly longer life and higher production efficiency.

Structural Features and Applicable Working Conditions of Long Drill Bits for Metal
Long drill bits for metal play a critical role in deep hole drilling and the machining of complex or hard-to-reach metal structures. Their primary advantages include extended cutting length, optimized chip-flute geometry, and improved stability that reduces deflection during deep drilling. These tools maintain consistent cutting performance across long distances, allowing operators to achieve higher hole straightness and dimensional accuracy. Long drill bits are widely used in mold manufacturing, aerospace structural components, hydraulic cylinder bodies, automotive housings, and other parts requiring deep holes or drilling across ribs or cavities. Selecting the correct long drill bit not only enhances machining quality but also reduces tool setup difficulty and increases overall process efficiency.
The Necessity of Long Drill Bits in Deep Position and Complex Part Machining
When drilling inside deep cavities, passing through rib structures, or navigating interference zones, long drill bits provide the extended cutting reach required to access the target area. Conventional drill bits often cannot reach these locations, but long drill bits maintain sufficient rigidity to complete the cutting task with reduced risk of bending or misalignment. In applications involving thicker sections or multi-layered metal structures, the longer tool length helps maintain hole straightness and reduces issues such as lateral drift, friction marks, and thermal deformation along the hole wall. Whether machining stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, or hardened steel, long drill bits significantly enhance controllability and consistency in deep hole machining tasks.
Long Drill Bit Rigidity, Chip Evacuation, and Vibration Control Methods
Longer tools naturally experience reduced rigidity, which makes proper vibration control and chip evacuation essential. The following key strategies improve drilling stability:
Enhanced Rigidity Design
High-grade long drill bits often incorporate reinforced shanks, tapered flute transitions, or premium base materials to increase resistance to bending and vibration. Higher rigidity results in improved straightness and reduced runout during deep drilling.
Optimized Chip-Flute Geometry
Long drill bits frequently feature deeper, smoother chip flutes to support continuous chip evacuation. Effective chip removal is essential for preventing heat buildup, avoiding chip packing, and maintaining a stable cutting load, particularly in “deep hole drilling tools for metal” applications.
Vibration and Runout Control
Controlled feed rates, gradual depth-in drilling strategies, and adequate coolant pressure help minimize vibration. Machine spindle runout should be tightly controlled to prevent tool chatter, premature wear, or micro-chipping.
Through proper design and parameter optimization, long drill bits maintain greater stability when machining tough materials such as steel, stainless steel, and high-strength alloys.
Different Operating Strategies for Long Drill Bits in Manual and CNC Machining
Long drill bits behave differently depending on the equipment used, requiring distinct strategies for manual tools versus CNC machines.
Manual Machining Strategies
When used on drill presses or handheld drilling equipment, maintaining stable axial pressure and minimizing lateral force are crucial. Lower cutting speeds, gradual feed, and frequent chip clearing reduce the risk of tool bending and overheating. Supplemental coolant application improves thermal control when drilling deeper holes or harder materials.
CNC Machining Strategies
CNC machines provide higher rigidity, controlled feed motions, and precise tool alignment. When combined with internal coolant delivery, peck drilling cycles, and optimized spindle parameters, long drill bits achieve superior accuracy and longer service life. In high-volume deep hole machining, internally cooled long drills or dedicated deep hole drilling tools deliver excellent reliability and sustained high-speed performance.
Regardless of the equipment type, proper tool selection, chip management, and cooling strategy are essential for maximizing the performance of long drill bits for metal.

Deep Hole Machining Solutions for Deep Hole Drilling Tools for Metal
Deep hole machining demands enhanced drilling stability, effective chip removal, and sufficient cooling capacity. When drilling depths exceed 10×D, 20×D, or even 30×D, factors such as rigidity, chip evacuation path, internal coolant channels, and surface coatings become critical. Depending on workpiece material, required hole depth, and accuracy expectations, solutions such as gun drills, BTA drills, and long deep hole drills are selected. In long-tail keyword scenarios such as “deep hole drilling bits for steel” or “deep hole drills for stainless steel,” tools must deliver high precision, stable chip evacuation, and safe cutting behavior—requirements common in mold manufacturing, aerospace components, hydraulic systems, and automotive parts.
Chip Removal Design and Cooling Methods in Deep Hole Drilling
Deep hole drilling presents challenges such as poor chip escape and rapid thermal buildup. Effective chip evacuation and cooling design directly impact machining success. Key features include:
Optimized Chip Channel Geometry
Deep, narrow, polished chip channels allow smooth chip flow and prevent blockages. Gun drills use a single cutting edge and guide pads to direct chips reliably along the flute.
High-Pressure Internal Coolant
Internal coolant systems deliver pressurized fluid to the cutting edge, reducing heat and flushing chips efficiently. This is essential when drilling deep holes in steel or heat-resistant alloys.
Chip Morphology Control
Cutting-edge geometry is engineered to create short, manageable chips, reducing the risk of chip wrapping or pocketing.
With proper coolant pressure, flute design, and chip-breaking geometry, deep hole drilling maintains a stable cutting environment and consistent hole quality.
Methods for Controlling Machining Stability and Hole Wall Quality
Due to the extreme drilling depth, maintaining stability and minimizing vibration are crucial for achieving smooth, straight hole walls. Common process control techniques include:
Enhanced Tool Rigidity
Solid carbide deep hole drills, gun drills, and reinforced long drills significantly reduce tool deflection and improve straightness.
Optimized Peck Drilling Cycles
Segmented drilling reduces cutting load and improves chip evacuation, particularly for difficult-to-machine materials.
Stable Machine and Fixturing
Deep hole machining requires precise spindle alignment, robust guide bushings, and rigid fixturing. Even minor misalignment can damage the hole wall.
Coatings for Improved Surface Finish
Coatings such as TiAlN or DLC reduce friction, enhance chip evacuation, and improve hole wall smoothness.
These methods ensure high-quality results even in demanding scenarios such as deep hole drilling in hardened steel, stainless steel, or aerospace alloys.
Application Examples in Mold, Aerospace, and Hydraulic Component Machining
Deep hole drilling tools are widely used in industries where precision and depth are essential:
Mold Industry
Cooling channels in injection and die-casting molds often require deep, precise holes. Deep hole drilling prevents misalignment and blockage issues.
Aerospace
Lightweight aerospace structures and engine components often require deep cavities or lubrication channels in high-strength alloys like titanium or Inconel.
Hydraulics and Automotive Components
Hydraulic cylinders and oil passages require long, straight holes with excellent sealing properties. Deep hole drilling provides consistent diameter and smooth internal surfaces.
These applications demonstrate the importance of deep hole drilling tools for metal in advanced manufacturing.

2025 CNC Parameters and Process Configurations for Efficient Metal Drilling
As metalworking moves toward higher efficiency, precision, and automation, proper CNC parameter selection and process configuration have become critical to drilling success. Whether using best drill bits for drilling metal, carbide drill bits for metal, long drill bits, or deep hole drilling tools, tool performance is strongly influenced by cutting parameters, chip management, and cooling strategies. By adapting parameters to material properties, hole depth, tool geometry, and machine rigidity, manufacturers can achieve longer tool life, improved hole quality, and more stable production cycles.
Matching Cutting Speed, Feed Rate, and Drilling Depth
Correct matching of speed (S), feed (F), and depth of cut ensures tool stability and efficient chip formation. Different metal drill bit types require different parameter ranges:
-
Carbide drill bits for metal support higher cutting speeds and are ideal for high-volume production and hard materials.
-
Long drill bits for metal require reduced spindle speeds and conservative feeds to minimize deflection.
-
Deep hole drilling tools require segmented drilling cycles and controlled feeds to prevent chip packing and heat accumulation.
Balancing workpiece hardness, hole depth ratio, tool diameter, and machine rigidity results in higher reliability and accuracy.
Impact of Optimal Cooling Strategies on Drill Bit Life
Cooling strategies directly influence temperature control, chip evacuation, and wear rate:
-
Internal coolant delivers high-pressure fluid to the tip, enhancing chip flow and heat reduction—especially crucial for deep hole drilling and carbide tooling.
-
External coolant works for shallow holes but is less effective in high-heat or deep drilling scenarios.
-
Even with advanced coatings, tools require stable coolant flow to achieve full performance.
Proper coolant pressure, volume, and fluid selection significantly extend tool life and reduce failure rates.
Parameter Reference for Different Drill Bit Types in Practical Machining
Different drill bit types require tailored machining strategies:
-
Carbide drill bits: High-speed, high-feed cutting; require rigid clamping and internal coolant for best results.
-
Long drill bits: Reduced speeds and feed rates; utilize steady feed, periodic chip clearing, and vibration control.
-
Deep hole drilling tools: For holes exceeding 3D–10D+, use high-pressure internal coolant and stable chip-removal cycles.
Developing parameter tables based on material, hole geometry, tool type, and equipment conditions significantly improves repeatability and machining quality.

How to Choose the Most Suitable Drill Bits for Different Machining Needs in 2025
In modern metalworking, selecting the correct drill bit is a decisive factor influencing machining efficiency, dimensional accuracy, and overall manufacturing cost. As industries face increasingly diverse materials—ranging from structural steel and stainless steel to hardened steel, aerospace-grade alloys, and heat-resistant superalloys—the requirements placed on drill bit materials, geometry, coatings, and cooling methods have become more complex. Likewise, machining scenarios involving deep holes, long aspect ratios, precision tolerances, or high-volume production demand a systematic, data-driven selection approach. By assessing tool performance, CNC parameter compatibility, machine rigidity, and production cycle expectations, manufacturers can choose the best drill bit configuration for each specific machining challenge.
Determining the Optimal Drill Bit Based on Material, Machining Depth, and Precision Requirements
Different metal materials and drilling depths impose unique demands on tool design and performance:
-
Carbon steel and alloy steel
High-performance coated drill bits offer a balanced solution for durability and efficiency, making them ideal for general-purpose machining. -
Stainless steel, high-hardness steel, and heat-resistant alloys
These materials require carbide drill bits for metal, which provide superior wear resistance, heat tolerance, and anti-chipping performance during high-load or continuous drilling. -
Deep hole machining (5D, 10D, 20D or greater)
Long drill bits for metal or dedicated deep hole drilling tools for metal are essential to ensure stability, maintain straightness, and achieve efficient chip evacuation throughout extended drilling depths. -
Precision machining with strict dimensional tolerances and high-quality hole walls
Drill bits featuring optimized cutting-edge geometry, high-toughness tool materials, and compatibility with internal coolant systems provide the best results when combined with accurate CNC parameter control.
By incorporating material properties, hole-depth requirements, cooling method, and accuracy demands into a structured selection model, engineers can quickly determine the most suitable drill bit for each application.
Developing a Drill Bit Procurement Strategy Based on the Production Environment
An effective procurement strategy should consider not only the tool specifications but also long-term operational cost and overall production workflow:
-
Batch production environments
Prioritize carbide drill bits with stable tool life and high repeatability. Partnering with reliable OEM drill bit suppliers ensures consistent quality, predictable performance, and optimal after-sales support. -
High-mix, low-volume machining
Choose versatile tool combinations with broad parameter adaptability to reduce tool-change frequency, inventory load, and setup costs. -
Compatibility with equipment capabilities
High-speed machining centers, high-rigidity CNC machines, and conventional equipment have different tool performance thresholds. Drill bit selection must match spindle power, rigidity, coolant pressure, and toolholding stability to avoid premature wear or tool breakage.
By integrating equipment conditions, production capacity, tool life cycles, and quality control requirements into the procurement framework, manufacturers can achieve a more efficient and cost-effective tool management system.
Comprehensive Tool Configuration Recommendations for Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement
Achieving optimal cost-performance requires aligning tool selection, cutting parameters, and process optimization into a continuous improvement loop:
-
Use application-specific tool combinations
For example:
– Coated drill bits for standard hole-making
– Carbide drill bits for metal for difficult-to-cut materials
– Deep hole drilling tools for long or high-precision holes
This targeted configuration increases overall tool applicability and reduces unnecessary waste. -
Maximize tool life through optimized parameters
Fine-tuning cutting speed, feed rate, and cooling strategy minimizes chipping, reduces downtime, and ensures more stable machining cycles. -
Implement standardized tool life management and data-driven monitoring
Real-time data collection enables predictive maintenance, reduces tool scrap, and enhances production repeatability.
This balanced tool configuration philosophy—focused on efficiency, cost control, and quality consistency—provides measurable benefits for production lines, including increased capacity, reduced machine load, and continuous process optimization.