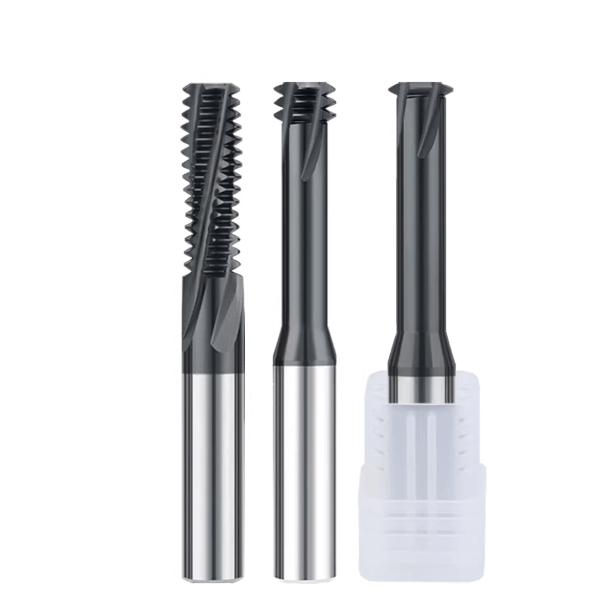
In high-precision thread machining, selecting the right thread milling cutter is crucial for both machining efficiency and thread quality. This is especially true when machining 304 and 316 stainless steel, where the material’s high ductility and work-hardening characteristics often pose challenges to thread surface quality and tool life. Using a suitable carbide thread milling cutter, combined with optimized cutting parameters, can significantly improve thread accuracy, reduce burrs, minimize tool breakage risks, and extend tool life.
For more demanding applications involving hardened or stainless steel, HRC55 thread milling cutters demonstrate excellent wear resistance and stability. Their special hardness and coating design maintain consistent thread dimensions during continuous machining, reducing the need for rework and lowering scrap rates. These cutters are particularly reliable in deep-hole or fine-pitch thread machining, effectively addressing issues related to poor chip evacuation and thread deformation.
From a procurement and supply chain perspective, choosing an experienced thread milling cutter manufacturer ensures more consistent tool quality. Manufacturers can also provide customized solutions for different stainless steel materials and thread pitches. Proper tool selection and parameter settings are key to maintaining machining efficiency, achieving high surface finish, and controlling costs. These factors are essential for achieving consistency in batch production while reducing production risks.

Analysis of Core Challenges in 304 and 316 Stainless Steel Thread Machining
Due to their high ductility and corrosion resistance, 304 and 316 stainless steels are prone to work hardening and material adhesion during thread machining. These materials often produce continuous chips that adhere to the tool surface, increasing cutting resistance and affecting thread accuracy and surface finish. When using solid carbide tools or HRC55 thread milling cutters, properly controlling cutting parameters and cooling conditions can significantly reduce the risk of material adhesion and improve machining stability.
Additionally, stainless steel’s low thermal conductivity causes the tool-workpiece interface temperature to rise during cutting, accelerating tool wear and coating failure. In deep-hole or fine-pitch thread machining, poor chip evacuation can easily lead to tool breakage or thread deformation. Therefore, selecting a carbide thread milling cutter that matches the pitch, thread length, and machine tool rigidity is essential to ensure a stable and reliable machining process.
The Impact of Material Adhesion on Thread Milling Cutters
Material adhesion is especially significant when machining 304 or 316 stainless steel, often causing rapid cutting-edge wear and increasing thread surface roughness. Using coated HRC55 thread milling cutters or high-performance carbide thread milling cutters can minimize adhesion and improve cutting efficiency. Adjusting feed rate, cutting depth, and cutting fluid type further mitigates adhesion issues and maintains stable cutting over extended operations.
Tool geometry and cutting-edge design also play a crucial role in reducing adhesion. Tools with helical or progressive cutting edges improve chip evacuation and reduce localized heat buildup, which in turn lowers tool wear and enhances thread consistency. This design is particularly valuable in high-volume production environments.
The Challenges of Work Hardening on Thread Accuracy and Tool Life
Stainless steel is prone to localized work hardening during cutting, increasing the cutting forces on the tool and accelerating wear. HRC55 thread milling cutters maintain their cutting capability even in hardened regions, allowing machining with lower forces while maintaining thread dimensions. Proper selection of cutting parameters and feed strategies is critical to ensuring both tool life and thread accuracy.
Work hardening also increases residual stress on the thread surface. Uncontrolled tool loads can lead to thread profile deformation or tooth damage. In practice, combining the wear resistance and rigidity of carbide thread milling cutters with multi-pass or multi-revolution cutting strategies can reduce the impact of hardening on thread quality. This approach ensures production efficiency and consistent results.
Chip Evacuation and Tool Breakage Risks in Deep-Hole Internal Thread Machining
Deep-hole internal thread machining often suffers from poor chip evacuation. Accumulated chips increase cutting temperatures, accelerate tool wear, and raise the risk of breakage. Using spiral-groove optimized carbide thread milling cutters or customized HRC55 thread milling cutters improves chip evacuation efficiency and reduces uneven tool stress. Combined with proper cutting fluid application and tool path strategies, this ensures accurate thread profiles and surface finishes.
For deep holes and fine-pitch threads, controlling the radial and axial cutting depth of each pass, along with optimizing tool rotation direction and feed path, effectively reduces tool breakage risks. Choosing an experienced thread milling cutter manufacturer for customized tools ensures precise tool geometry and wear resistance, further minimizing production interruptions and scrap rates while improving efficiency and cost control.

Selection Logic for Thread Milling Cutters in Stainless Steel Thread Machining
In stainless steel thread machining, rational tool selection is key to processing efficiency, thread accuracy, and tool longevity. 304 and 316 stainless steels have high ductility and work-hardening tendencies, making tool wear resistance, rigidity, and chip evacuation capabilities critical. Prioritizing integral carbide thread milling cutters maintains high-precision thread machining while effectively managing thermal loads and cutting force variations from deep-hole machining and multi-pass operations.
Different thread diameters, pitches, and lengths place varying demands on tool geometry and cutting edge design. Single-tooth, double-tooth, and multi-tooth designs differ in cutting force distribution, chip evacuation efficiency, and tool life. Considering machine tool rigidity, fixture stability, and production volume ensures consistent, high-efficiency machining and reduces tool wear and scrap. This also guides selection of a reliable thread milling cutter manufacturer.
Stability Advantages of Integral Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
Integral carbide thread milling cutters offer high rigidity and wear resistance, maintaining thread size stability during continuous machining. Compared to multi-segment tools, they reduce radial vibration and thread profile errors. High-performance coatings and carbide substrates extend tool life and lower thread surface roughness, particularly in deep-hole or hardened-section machining.
The integral design minimizes tool interface gaps and cumulative errors, improving multi-pass cutting stability. In high-volume production, these tools provide consistent results, reduce scrap rates, and lower tool change frequency, ensuring both processing cost control and production efficiency.
Application Scenarios of Single-Tooth and Multi-Tooth Thread Milling Cutters
Single-tooth thread milling cutters excel in fine-pitch and high-precision applications, offering better chip evacuation and cutting stability. They are ideal for deep-hole or small-diameter threads, reducing heat accumulation and tool wear. Multi-tooth cutters are better suited for high-speed batch machining of medium to large-diameter threads, dispersing cutting forces and reducing machine load while maintaining efficiency.
Tool choice should consider thread depth, hole diameter, machine rigidity, and production volume. Proper tooth count and pitch improve thread surface quality and extend the life of carbide thread milling cutters, providing reliable mass-production performance.
Tool Structure Selection for Small Diameter and Fine-Pitch Threads
For small-diameter or fine-pitch threads, tool geometry and cutting-edge design directly affect accuracy and surface quality. Optimized HRC55 thread milling cutters or high-performance carbide thread milling cutters allow machining with lower cutting forces, reducing thread deformation and burr formation. Proper helix angle, rake angle, and relief angle improve chip evacuation and wear resistance.
For deep-hole or long threads, guide grooves or helical cutting grooves improve chip flow and reduce tool breakage risk. Combined with precise feed strategies and cutting parameters, this ensures machining stability and thread consistency, supporting high-precision stainless steel component production.

Practical Application Performance of HRC55 Thread Milling Cutters in 304/316 Stainless Steel
When machining 304 and 316 stainless steel, the material’s high ductility and work-hardening tendencies place high demands on thread accuracy and tool life. HRC55 thread milling cutters, with their high hardness and toughness, maintain stable cutting forces in high-load conditions. This reduces tool wear and ensures consistent thread dimensions. By matching cutting parameters and tool structure appropriately, burrs and surface irregularities can be minimized, improving overall thread surface finish.
In long-thread or deep-hole machining, the high rigidity and wear resistance of HRC55 tools support continuous multi-pass milling. Combined with high-performance carbide thread milling cutters, this approach enhances heat resistance, prevents material adhesion, and reduces tool replacement frequency. As a result, production efficiency is improved, providing reliable support for manufacturing high-precision stainless steel components.
Advantages of HRC55 Hardness in Counteracting Work Hardening in Stainless Steel Machining
During stainless steel machining, localized work hardening can increase cutting resistance and tool wear. HRC55 thread milling cutters maintain edge integrity even in high-stress areas, reducing the impact of work hardening on thread accuracy. Optimizing cutting parameters and using carbide thread milling cutters with a solid alloy design allows for stable cutting forces during continuous operations, reducing thread profile deformation and burrs.
The hardness advantage of HRC55 is particularly beneficial in small-diameter and fine-pitch thread machining. It maintains tool sharpness without raising cutting temperatures, improves chip evacuation efficiency, and ensures thread accuracy. These features extend tool life and provide reliable performance for high-precision, mass-production operations, including deep-hole threads.
Life Performance of HRC55 Thread Milling Cutters in Continuous Machining
Continuous machining and multi-pass milling can cause heat accumulation and cutting force fluctuations, leading to accelerated wear or edge chipping. HRC55 thread milling cutters offer excellent wear resistance and rigidity, maintaining stable cutting over prolonged operations and significantly extending tool life. Proper control of radial and axial cutting depths can make tool life several times longer than that of traditional tools, improving efficiency and lowering production costs.
In batch processing or high-load thread milling, HRC55 cutters maintain consistent thread dimensions and surface quality. When combined with high-performance carbide thread milling cutters, thread machining is further optimized, achieving efficient, stable operations for deep-hole and complex thread applications.
Suitable Coating and Edge Treatment for Stainless Steel Machining
Tool coatings and edge treatments play a decisive role in wear resistance and anti-sticking performance. High-hardness coatings such as TiAlN or AlTiN on carbide thread milling cutters reduce friction and heat accumulation, improving thread surface finish and accuracy. For HRC55 cutters, optimizing edge treatment—such as micro-chamfering or tool tip radius design—enhances chip evacuation, minimizing burrs and thread deformation.
Combined with appropriate cutting fluids and cooling methods, optimized coatings and edge geometry maximize performance in deep-hole, fine-pitch, or small-diameter threads. Considering tool hardness, coating quality, and edge design together ensures stable, high-efficiency, high-precision stainless steel thread machining, while extending tool life and supporting reliable production.

Recommended Cutting Parameters for 304/316 Stainless Steel Thread Machining
Appropriate cutting parameters are critical for ensuring thread accuracy, tool life, and surface finish. Thread depth, hole diameter, and pitch affect cutting forces and chip evacuation. When using HRC55 or carbide thread milling cutters, spindle speed, feed rate, cutting depth, and pitch compensation should be optimized for the machining conditions. Correct parameter selection reduces cutting heat, lowers tool wear, and ensures consistent thread dimensions during multi-pass milling. Optimized parameters also improve production efficiency and reduce burrs, especially in deep-hole or small-diameter threads. Experienced thread milling cutter manufacturers can provide guidance on parameter matching, improving reliability and cost control in mass production.
Principles for Setting Thread Milling Cutter Speed and Feed Rate
Speed and feed rate are core factors affecting tool life and thread quality. When using HRC55 thread milling cutters, spindle speed should ensure stable cutting while avoiding heat-induced tool wear or thread deviations. Feed rate should consider thread diameter, pitch, and machine rigidity. Excessive feed increases cutting forces; too low a feed reduces production efficiency.
High-performance carbide thread milling cutters support stable chip evacuation while maintaining sharpness. A balanced combination of speed and feed reduces tool adhesion and cutting vibration, ensuring smooth thread machining and extending tool life, particularly in mass production.
Safe Range for Radial and Axial Cutting Depth
Radial and axial cutting depth directly affect tool load and machining stability. For HRC55 cutters in 304/316 stainless steel, cutting depths must avoid excessive radial forces that can cause wear or chipping. Proper depth selection ensures thread accuracy, improves chip evacuation, and reduces burrs.
In multi-pass or deep-hole machining, layered axial depth control reduces peak cutting forces and thermal load. Combined with the wear resistance and rigidity of carbide thread milling cutters, proper depth control significantly improves tool life and machining efficiency.
Pitch Compensation and Stability Control in Multi-Pass Thread Milling
Pitch compensation is critical, especially for deep-hole or fine-pitch threads. Accurate pitch compensation ensures thread profiles meet design dimensions, reducing thread errors and tooth damage. Combined with multi-pass milling, cutting forces are distributed, lowering single-pass load and maintaining machining stability.
Using tool path optimization, feed rate adjustment, and high-performance carbide thread milling cutters ensures precise pitch compensation. This approach maintains high-precision threads in mass production, extends tool life, and improves production efficiency and cost control.

Key Details for Improving Stainless Steel Thread Machining Quality
304/316 stainless steel demands high thread accuracy, surface finish, and tool life. Adhesion and work hardening can affect thread consistency and accelerate wear. Proper cooling strategies, optimized tool paths, and controlled cutting parameters maintain stable thread quality while extending tool life of HRC55 or carbide thread milling cutters.
In deep-hole, fine-pitch, or small-diameter machining, vibration, poor chip evacuation, and heat accumulation cause burrs and irregular threads. Optimizing tool structure, using pitch compensation, and applying multi-pass cutting reduces these issues, providing reliable solutions for high-precision stainless steel components while improving efficiency and cost control.
The Impact of Cooling Methods on Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
Cutting heat affects tool life and thread quality. High-performance coolant or high-pressure spray reduces cutting-edge temperature of HRC55 cutters, minimizing wear and adhesion. In deep-hole threads, high-pressure cooling improves chip evacuation, preventing accumulation that causes tool chipping or surface scratches.
Proper cooling also reduces work hardening, maintaining thread size consistency. Optimizing coolant flow with carbide thread milling cutters enhances machining stability and extends tool life, ensuring reliable high-precision thread production.
The Decisive Role of Tool Path on Thread Surface Quality
Tool paths affect thread flatness and machining efficiency. In deep-hole or fine-pitch threads, planning milling sequence and radial/axial tool paths reduces vibration and tool load, ensuring profile consistency. Optimized paths with HRC55 or carbide thread milling cutters reduce burrs and maintain thread accuracy.
Layered or helical cutting improves chip evacuation and reduces heat buildup. This strategy enhances thread surface finish and tool life, crucial for high-volume and high-precision production.
How to Avoid Burrs and Irregular Threads in Stainless Steel Thread Machining
Burrs and irregular threads result from excessive forces, tool wear, or poor chip evacuation. HRC55 cutters resist cutting loads and improve thread surface quality. Adjusting radial/axial depth and using pitch compensation reduces tooth damage and irregular deformation.
Combining high-performance carbide cutters with optimized cooling improves heat distribution and chip evacuation. Controlling tool path, multi-pass cutting, and coolant application reduces burrs and irregular threads, ensuring precision and consistent production.

Common Machining Problems and Corresponding Solutions for Thread Milling Cutters
In stainless steel thread machining, common issues include thread size deviations, tool wear, and poor chip evacuation. 304 and 316 stainless steels have high ductility and work-hardening tendencies, so improper cutting parameters, tool selection, or machining strategies can reduce thread accuracy and increase surface burrs. Using HRC55 thread milling cutters or high-performance carbide thread milling cutters, combined with experience from batch processing, can effectively reduce dimensional instability and abnormal tool wear.
Deep-hole internal threads and fine-pitch threads are particularly prone to poor chip evacuation, which increases cutting temperatures and tool breakage risk. By optimizing tool paths, applying pitch compensation, and using effective cooling methods, thread machining can be stabilized. This improves tool life, enhances surface quality, and ensures high consistency with low scrap rates in mass production.
Causes and Adjustment Methods for Unstable Thread Dimensions
Unstable thread dimensions are often caused by cutting force fluctuations, tool wear, or insufficient machine rigidity. Using HRC55 thread milling cutters maintains a high-hardness cutting edge, reducing cutting deformation. Fine-tuning spindle speed, feed rate, and cutting depth, along with optimizing multi-pass milling strategies, can ensure consistent thread dimensions.
Tool wear also contributes to reduced accuracy. Regular inspection and timely replacement or regrinding of carbide thread milling cutters prevent excessive thread profile deviations. Combining this with pitch compensation and proper tool path design further enhances thread stability in mass production.
Troubleshooting Abnormal Tool Wear or Chipping
Abnormal tool wear or chipping manifests as rough thread surfaces, increased burrs, or abnormal vibrations. For HRC55 thread milling cutters, check cutting parameters first, including spindle speed, feed rate, and cutting depth. When wear is severe, use high-performance carbide thread milling cutters for edge regrinding or replacement to restore machining stability.
Chip evacuation and machine tool rigidity are critical factors. Accumulated chips or unstable fixtures accelerate tool wear and increase chipping risk. Optimizing tool path, coolant application, and multi-pass strategies effectively reduces abnormal wear, improving machining consistency and batch production efficiency.
Strategies for Addressing Poor Chip Evacuation in Deep-Hole Internal Thread Machining
Deep-hole threads are prone to chip accumulation, increasing cutting forces, accelerating wear, and risking tool breakage. Using high-performance carbide thread milling cutters or HRC55 cutters with optimized helical flute design improves chip evacuation. High-pressure coolant or directed coolant jets further reduce cutting temperature and prevent clogging.
Layered cutting, shallow radial depth, and gradual axial advancement reduce tool load and improve chip evacuation. In mass production, these methods maintain thread dimensions and surface quality, extend tool life, reduce downtime, and enhance the stability and efficiency of stainless steel thread machining.

Key Indicators for Evaluating Thread Milling Cutter Manufacturers from a Machining Perspective
Tool quality directly impacts production efficiency, thread accuracy, and cost control in high-precision stainless steel thread machining. Choosing an experienced thread milling cutter manufacturer ensures high-consistency HRC55 or carbide thread milling cutters, maintaining stable thread dimensions and excellent surface finish. Assessing the manufacturer’s R&D capabilities, production processes, and quality control procedures is crucial for machining reliability.
Additionally, the manufacturer’s ability to provide customized tools and technical support for different pitches, thread diameters, and deep-hole machining is essential. High-quality manufacturers optimize cutting-edge geometry and parameters for complex or non-standard threads, improving machining stability, extending tool life, and reducing scrap rates, thus lowering production costs in mass production.
The Importance of Tool Consistency in High-Volume Stainless Steel Machining
In high-volume production, tool consistency determines thread accuracy and surface quality. Even high-performance HRC55 cutters may vary in geometry between batches, causing profile deviations, burrs, or irregular threads. Consistent tools ensure uniform accuracy and finish for every thread, reducing rework and enhancing production efficiency.
Tool consistency also affects machining costs. Stable carbide thread milling cutters reduce tool changes and downtime, particularly for deep-hole or fine-pitch threads. Choosing a reputable thread milling cutter manufacturer ensures highly consistent tools, supporting smooth production and lowering overall costs.
Thread Milling Cutter Manufacturer’s Ability to Customize Cutting Edge Geometry and Parameters
Optimizing cutting-edge geometry and parameters for different stainless steel materials and thread sizes is key for quality. Experienced manufacturers can customize HRC55 or carbide thread milling cutters based on pitch, thread depth, and machine rigidity, achieving optimal cutting force distribution and chip evacuation. Customized tools maintain accuracy and surface finish in small-diameter, deep-hole, or fine threads while extending tool life.
Customized cutting angles, helix groove designs, and coating schemes address work-hardening and stainless steel challenges. In practice, these tools improve machining stability and meet mass-production requirements, reducing risks and improving efficiency.
The Impact of Stable Delivery Times and Technical Support on Production Efficiency
Reliable delivery times are essential for high-volume production. Choosing a trustworthy thread milling cutter manufacturer ensures timely delivery of HRC55 or carbide cutters, preventing stoppages due to tool shortages and improving production efficiency.
Comprehensive technical support helps optimize cutting parameters, tool paths, and usage strategies. Working with manufacturer engineers to address chip evacuation, tool wear, or thread accuracy issues improves machining quality, reduces production risks, and ensures stable mass production with high consistency.

Comprehensive Cost Control of Thread Milling Cutters in Stainless Steel Thread Machining
Tool selection, parameter optimization, and production management directly affect unit cost and efficiency. Although high-performance HRC55 or carbide cutters may have a higher initial price, extended tool life, lower scrap rates, and optimized tool paths reduce the actual cost per thread. Proper tool management ensures accuracy, surface quality, and production stability, delivering low overall costs for high-precision machining.
Combining experienced manufacturers with customized tool solutions optimizes geometry, parameters, and chip removal, reducing breakage, burrs, and size deviations in deep-hole, fine-pitch, and small-diameter threads. Considering tool life, accuracy, efficiency, and replacement frequency balances high-quality machining with cost control, providing long-term economic benefits.
Relationship between Single Tool Life and Unit Thread Cost
Tool life determines the cost per thread. Long-life HRC55 or carbide cutters minimize costs by reducing tool changes and downtime. In deep-hole or fine-pitch machining, high wear resistance and efficient chip removal are critical for maintaining stable dimensions and surface finish.
Monitoring tool usage, planning cutting parameters, and optimizing tool paths extend tool life and reduce scrap. Unit thread cost depends not only on tool material but also on cutting strategy, cooling, and production management—key factors for precision and cost efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison of HRC55 and Standard Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
Compared to standard carbide cutters, HRC55 cutters have a slightly higher initial cost but longer life and more stable thread quality. They reduce breakage, burrs, and size deviations, lowering downtime and rework, particularly for deep-hole, fine-pitch, or small-diameter threads.
Standard carbide cutters are cost-effective for light-duty or low-volume machining, but may not meet continuous production requirements. Considering efficiency, accuracy, and replacement frequency, HRC55 cutters provide long-term cost optimization and reliable high-precision performance.
How to Reduce Tool Changes and Downtime Through Proper Tool Selection
Proper tool selection reduces tool changes and downtime. Selecting the right HRC55 or carbide cutter for specific thread diameters, depths, and pitches optimizes cutting force distribution and chip evacuation. Matching teeth number, cutting edge type, and coating improves stability and thread quality.
Combining production planning and cooling strategies, rational scheduling of tool usage and replacement minimizes downtime and production costs while ensuring machining accuracy. Scientific tool selection and lifecycle management improve efficiency and ensure economic benefits for high-precision stainless steel thread machining.